The Secrets of Global Education: Exploring the Education Systems in the UK, US, Canada, and Australia
While selecting a study destination, it is essential to have a basic understanding of the various educational systems. This article aims to provide you a comprehensive understanding of the education systems of four countries: the UK, US, Canada, and Australia by analyzing the educational structures of these countries in light of the unique lifestyles and academic environments. This will help you determine the best path for your academic journey.
UK Education System
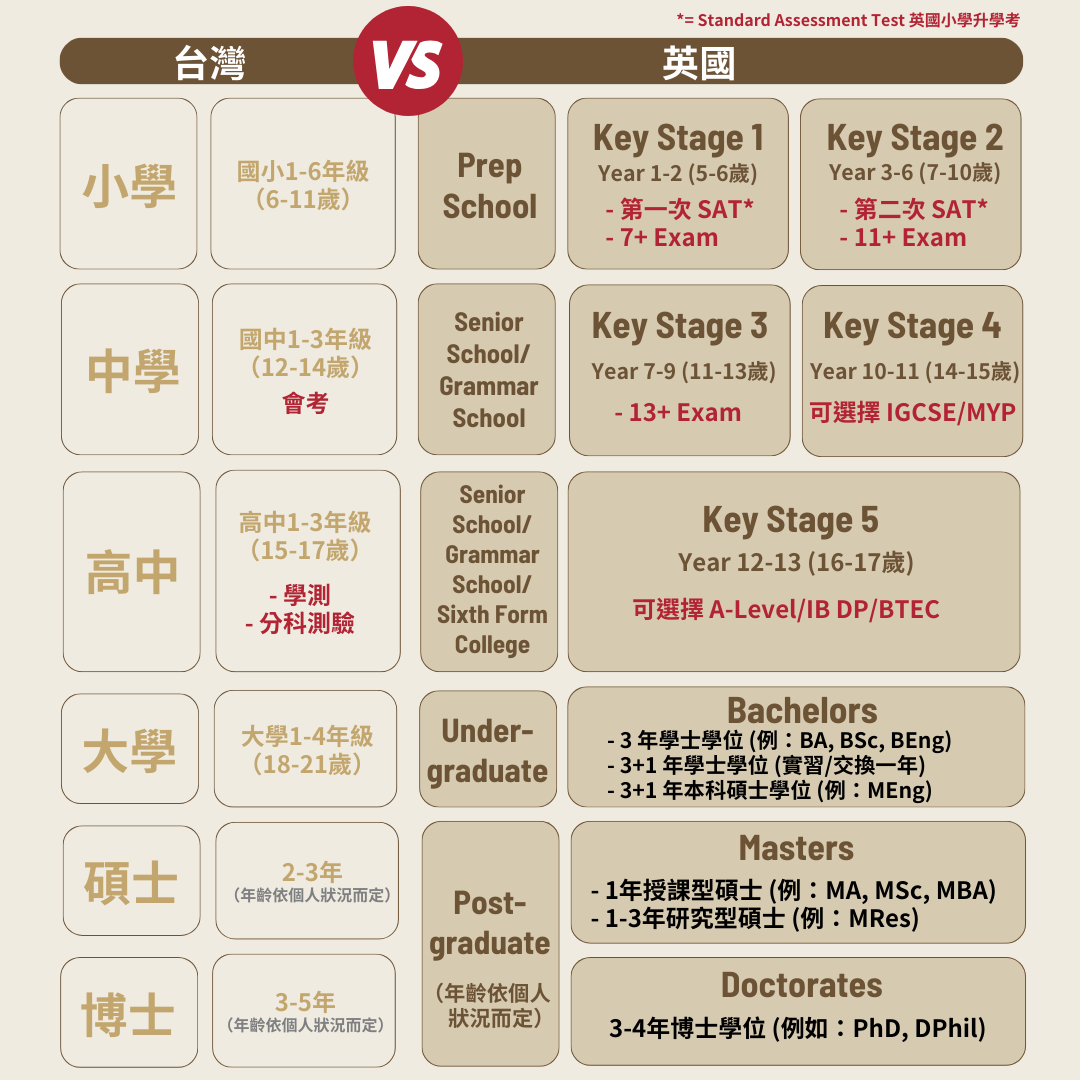
The UK is well-known for its outstanding education and boasts a rich educational heritage as well as a broad academic system that provides students with a wide range of learning options. The following will outline the fundamental structures of the UK education system, including educational levels, entrance exams, and special education courses.
UK Educational Levels:
Nursery:
- Nursery is the first stage of education in the UK, often beginning at ages 3 to 4, and focuses on developing social skills and core cognitive development.
Primary School:
- Pupils in primary school learn fundamental subjects including math, science, English, and social studies from Year 1 to Year 6.
Secondary School:
- Secondary school includes Years 7 to 11, with an emphasis on in-depth study of subjects and general student development.
Sixth Form College:
- Sixth Form College includes Years 12 to 13, allowing students to concentrate on fewer subjects while preparing for university entrance exams.
Main Entrance Examinations in the UK:
- Prep School Entrance Exam (7+ Exam): Taken at the age of 7.
- Grammar School Entrance Exam (11+ Exam): Taken at the age of 11.
- Common Entrance Exam for independent schools: Taken at the age of 13.
- SATs: National entrance exams for secondary school, administered at end of Year 6.
- CAT4: An annual examination of students’ academic potential and developmental capacities, designed for students aged 6 to 17, is a standard cognitive ability testing system used by independent schools in the UK.
- The GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education) is the main examination taken by British students at the age of 16, including a variety of courses, and the results influence students’ future study options.
- A-Level (Advanced Level): Examinations taken by British high school students at the age of 18, typically covering 2 to 3 subjects and serving as a primary indicator of academic ability during university admissions process. The British high school curriculum spans two years; students typically choose 4 to 5 subjects in the first year (AS level) and then drop subjects they are less proficient in based on their learning condition.
- Business & Technology Education Council (BTEC): A vocational education system in the UK. BTEC-Level 3 is equivalent to A-Level. Most universities in the UK (excluding medical schools) accept BTEC qualifications for admissions, however, individual departments may require certain BTEC course credentials.
- IB (International Baccalaureate): An internationally recognized academic program where students are required to study 6 subjects and earn a diploma through IB examinations.
UK Educational Features:
Boarding Schools:
The UK has numerous renowned boarding schools that provide students with round-the-clock learning and living environments, emphasizing both academic and moral development.
Pre-University Courses:
High school A-Level and IB courses are considered pre-university courses, offering students advanced subject knowledge to prepare for university study.
Arts and Sports Education:
British schools encourage students to participate in arts and sports activities, providing various training and competition opportunities.
The British education system combines traditional teaching methods with modern educational concepts, emphasizing students’ holistic development and talent cultivation. This diversity makes the UK one of the favored educational destinations for many students and their parents.
Compare to Taiwan’s educational structure:
| TAIWAN | UK |
|---|---|
| Elementary School Grade 1-6 (age 7-12) |
Primary Education Year 1-6 (5-10 years old): First Level: Similar to grades 1 and 2 in Taiwan, called Year 1 and Year 2. Second Level: Similar to grades 3 to 6 in Taiwan, called Year 3 to Year 6. |
| Jinior High Shcool Grade 7-9 (age 13-15) |
Secondary Education: First Level: Secondary School grade 1-3 (age 11-13). Second Level: GCSE grade 4-5 (age 14-15) and A Level / AS Level grade 6 (age 16-17). GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education): |
| Senior High School Grade 10-12 (age 16-18) |
|
| University 1-4 (age 19-22) |
Bachelor Degrees: The duration of a university degree is generally three years. If the course includes corporate internships or overseas exchange student programs, it will be extended to four years. Generally, the third year is internship or exchange, and the fourth year returns to school to complete studies. For some specific departments, such as medicine, architecture, etc., the study time may be longer. The academic system in Scotland is different from that in other parts of the UK. It is generally a four-year university program. |
| Master 1-2 (age: depends) |
Diploma / Certificate: The duration is about 9 months, mainly lecture-based teaching. The admission threshold is comparatively low. Taught Master: The duration is about 12 months. The most favored choice for Taiwanese people. Research Master: The duration is about 1-3 years. No required courses, mainly research and discussion between students and professors. |
| Phd 3-5 years (age: depends) |
Doctoral Degree: The duration is 3 years and can be up to 7 years, mainly focusing on thesis research. New Route PhD: The duration is usually 4 years, combining research and lectures. Professional / Taught doctorate: The duration is usually 3 years, focusing on professional subject areas. |
Advantages: The UK has a long history and rich culture. Since the British system emphasizes professional training, the learning content is not only relatively profound, but also a degree can be obtained in a shorter time, making it suitable for students who have a clear direction. In addition, there are a variety of visas you can apply for after graduating from university, which are suitable for international students who plan to live in Europe for a long time.
Disadvantages: Intensive courses also represent heavy academic pressure, low degree of freedom in course selection, and high threshold for changing majors.
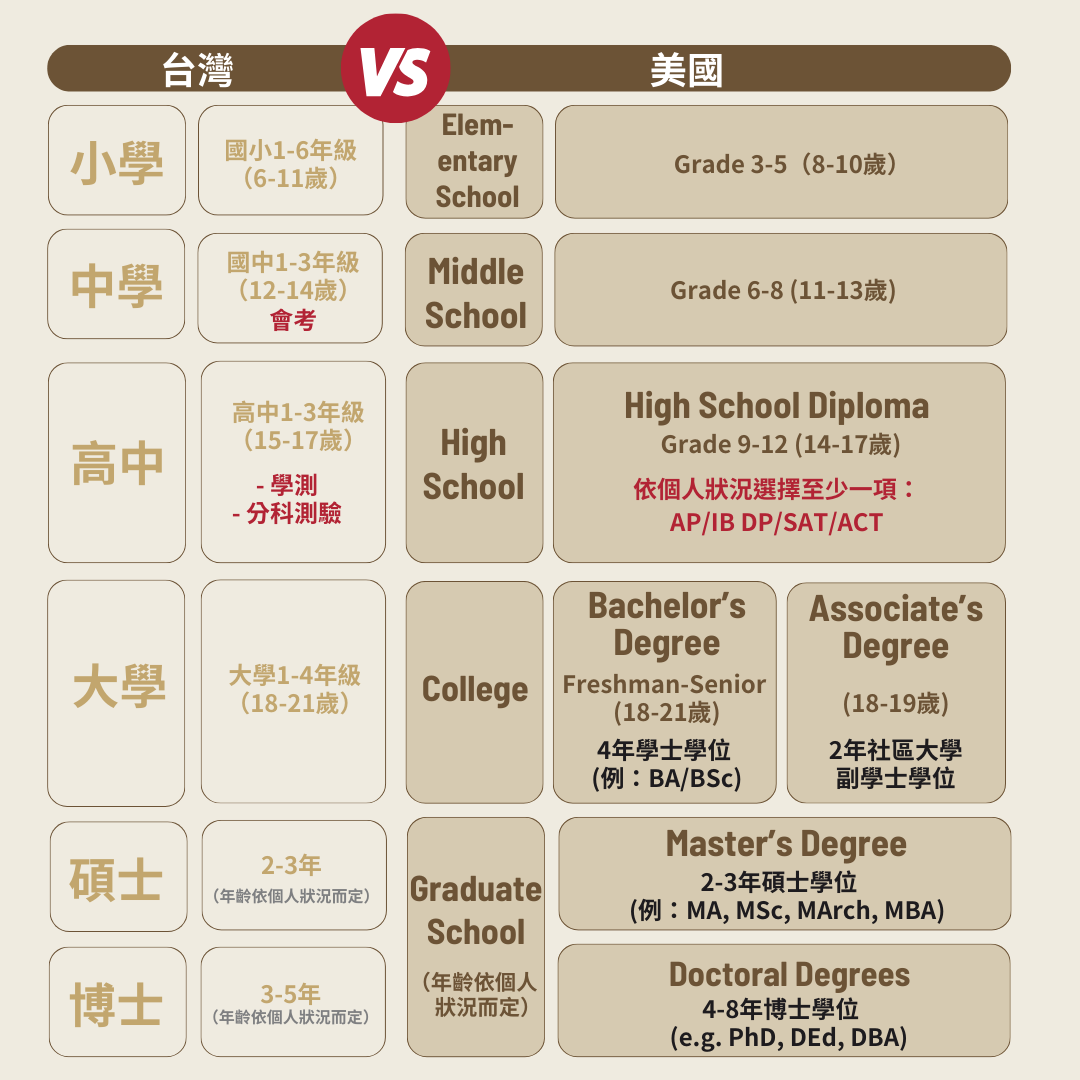
US education system
The US has one of the most diverse and open education systems in the world, which not only provides a wide range of choices and opportunities, but also helps students further develop in their studies and interests. The following will introduce the basic structure of the American academic system, including academic levels, entrance examinations and special education courses.
US Educational Levels:
Kindergarten:
- Kindergarten provides basic education for children aged 3 to 5 years old, helping them develop social skills and study habits.
Elementary School:
- Elementary school includes grades 1 to 5, teaching basic subjects such as mathematics, English, science and social studies to build a solid knowledge base for students.
Middle School:
- Middle school includes grades 6 to 8. In addition to focusing on subject expansion and elective courses, it also cultivates students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
High School:
- High school consists of grades 9 to 12, where students can choose more elective courses and begin preparing for college education or careers.
Main Entrance Examinations in the US:
SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test):
- A widely accepted college entrance exam covering reading, writing, and math. Scores are typically used for college applications.
ACT (American College Testing):
- Another college entrance exam covering English, math, reading, and science. Many schools accept ACT scores as one of the admission criteria.
AP Exams (Advanced Placement Exams):
- Exams administered by the College Board. Due to the wide range and challenge of the examination, students can exchange their obtained scores for university credits.
US Educational Features:
AP courses (Advanced Placement Courses):
- A series of high-level subjects offered by high schools, allowing students to gain access to college-level courses in high school. Students can earn college credit by taking AP exams.
IB Course (International Baccalaureate Program):
- An international academic course designed to cultivate students’ international perspective and comprehensive competency. It includes high school and pre-university courses.
Elective Courses:
- High school students can choose to take specific subjects based on their interests and goals to further develop their specialties and majors.
The American education system emphasizes students’ individuality and diversity and provides various pathways for further education and career development. Students can choose an education path that suits them based on their personal interests and talents, laying a solid foundation for future development.
- One-year Certificate Programs:
Designed to provide training in specific vocational skills. - Two-year Diploma Programs:
Focus on specific vocational skills or technical training. - Three-year Advanced Diploma Programs:
Focus on specific vocational skills or technical training. - Two-year Associate’s Degree:
Offered by community colleges. - Four-year Bachelor’s Degree:
Different degree types are offered, such as Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Science. - 1 to 2-year Post-Baccalaureate Certificate:
Offers students holding a bachelor’s degree the option of further professional training. These diploma and degree options offer a variety of study and career development opportunities, allowing students to choose based on their needs and goals.
Compare to Taiwan’s educational structure:
| Taiwan | US |
|---|---|
| Elementary School Grade 1-6 (age 7-12) |
Elementary School 1-5 (age 6-10) |
| Jinior High Shcool Grade 7-9 (age 13-15) |
Middle School 6-8 (age11-13) |
| Senior High School Grade 10-12 (age 16-18) |
High School 9-12 (age 14-17) |
| University 1-4 (age 19-22) |
Certificate Programs: Designed to provide training in specific vocational skills. Diploma Programs: Advanced Diploma Programs: Associate’s Degree: Bachelor’s Degree: Post-Baccalaureate Certificate: |
| Master 1-2 (age: depends) |
Master’s Degree |
| Phd 3-5 years (age: depends) |
Doctoral Degree |
Advantages: The American academic system attaches great importance to the holistic development of individuals and encourages students to develop the ability to learn independently and innovate. This educational philosophy is also reflected in the United States’ diverse curriculum choices and flexible department transfer policies. As the home of the world’s top universities, the United States also provides abundant scholarship opportunities to attract outstanding talents from around the world.
Disadvantages Your chances of admission to some universities will be impacted if you decide to apply for financial aid. If you want to attend the best universities in the country, you may have to deal with intense competition and tedious application preparation work. Some of the tasks include keeping track of your extracurricular activities, writing more than 10 essays for different universities, learning about the policies and traditions of each university, and getting ready for interviews, etc. Furthermore, the cost of studying abroad can differ significantly depending on the school or region, and there are high requirements for different types of visas.
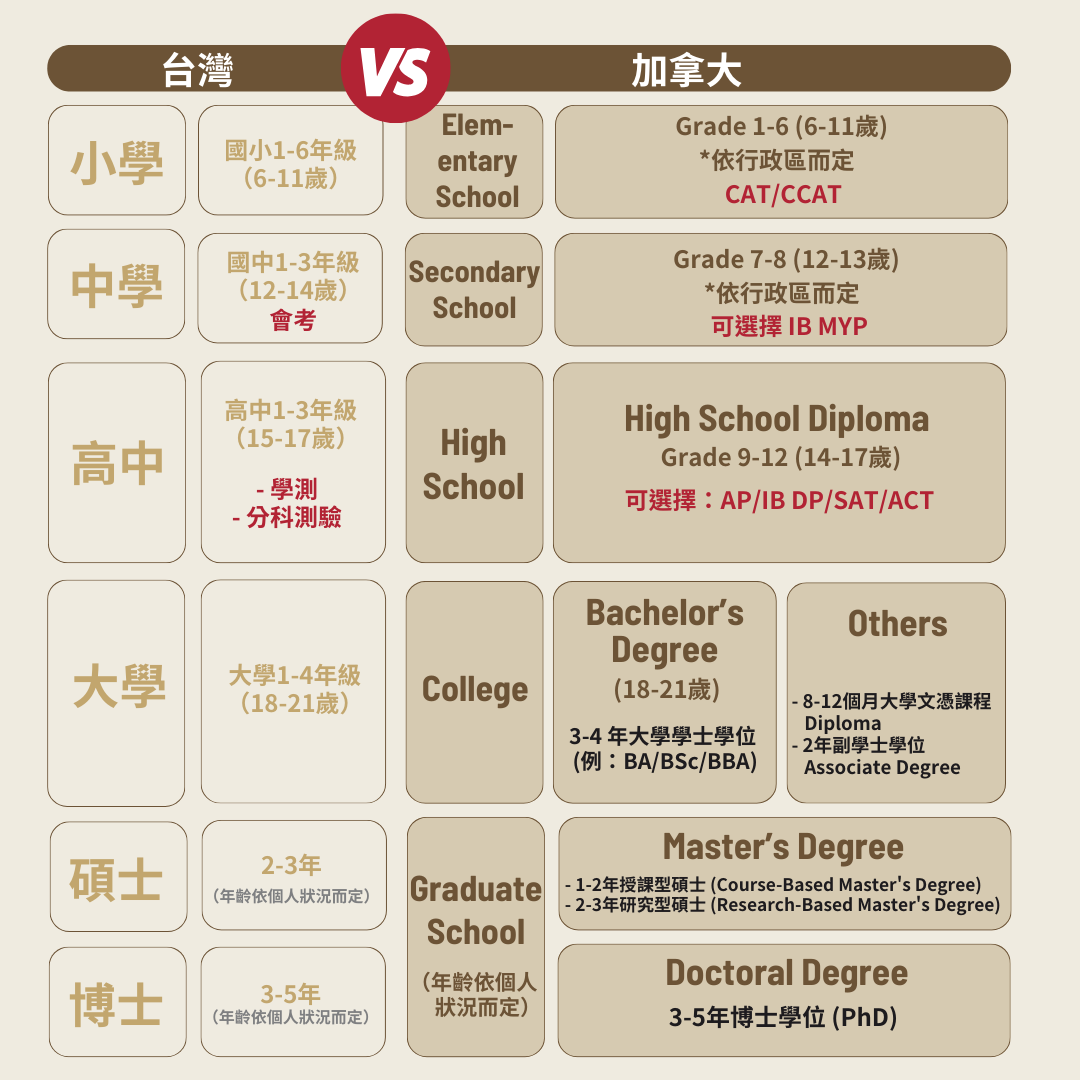
Taiwan’s education system vs. Canadian education system
In Canada, the educational system closely resembles that of the United States, offering students a diverse array of educational pathways. Additionally, the livable environment and relatively open immigration policies are significant factors that attract international students to pursue their studies in Canada. Below is a detailed overview and analysis of the Canadian education system, including its advantages and disadvantages.
| Taiwan | Canada |
|---|---|
| Elementary School Grade 1-6 (age 7-12) |
Elementary Education:Grade 1-8 (age 6-13) Secondary Education:Grade 9-12 (age 14-17) |
| Jinior High Shcool Grade 7-9 (age 13-15) |
|
| Senior High School Grade 10-12 (age 16-18) |
|
| University 1-4 (age 19-22) |
Certificate Programs: Designed to provide training in specific vocational skills. Diploma Programs: Focus on specific vocational skills or technical training. Advanced Diploma Programs: Focus on specific vocational skills or technical training. Associate’s Degree: Offered by community colleges. Bachelor’s Degree: Different degree types are offered, such as Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Science. Post-Baccalaureate Certificate: Offers students holding a bachelor’s degree the option of further professional training. |
| Master 1-2 (age: depends) |
Master’s Degree |
| Phd 3-5 years (age: depends) |
Doctoral Degree |
Advantages: The social environment and public security in Canada are outstanding and the country’s citizens are generally friendly and gentle. The numerous opportunities for employment and education provided by CO-OP minimize the financial burden of education. Studying overseas in Canada has a lower cost than studying in the US or the UK. Because of its proximity to the United States, it has the advantage of connecting education and employment opportunities in the US. When combined with the welcoming immigration laws, it’s an ideal location to study for people who enjoy North American culture.
Disadvantages: Since most universities are public, applying for scholarships can be challenging. In comparison to the US and the UK, there are fewer university options. You must get used to the bitter cold and snowy conditions of the area.
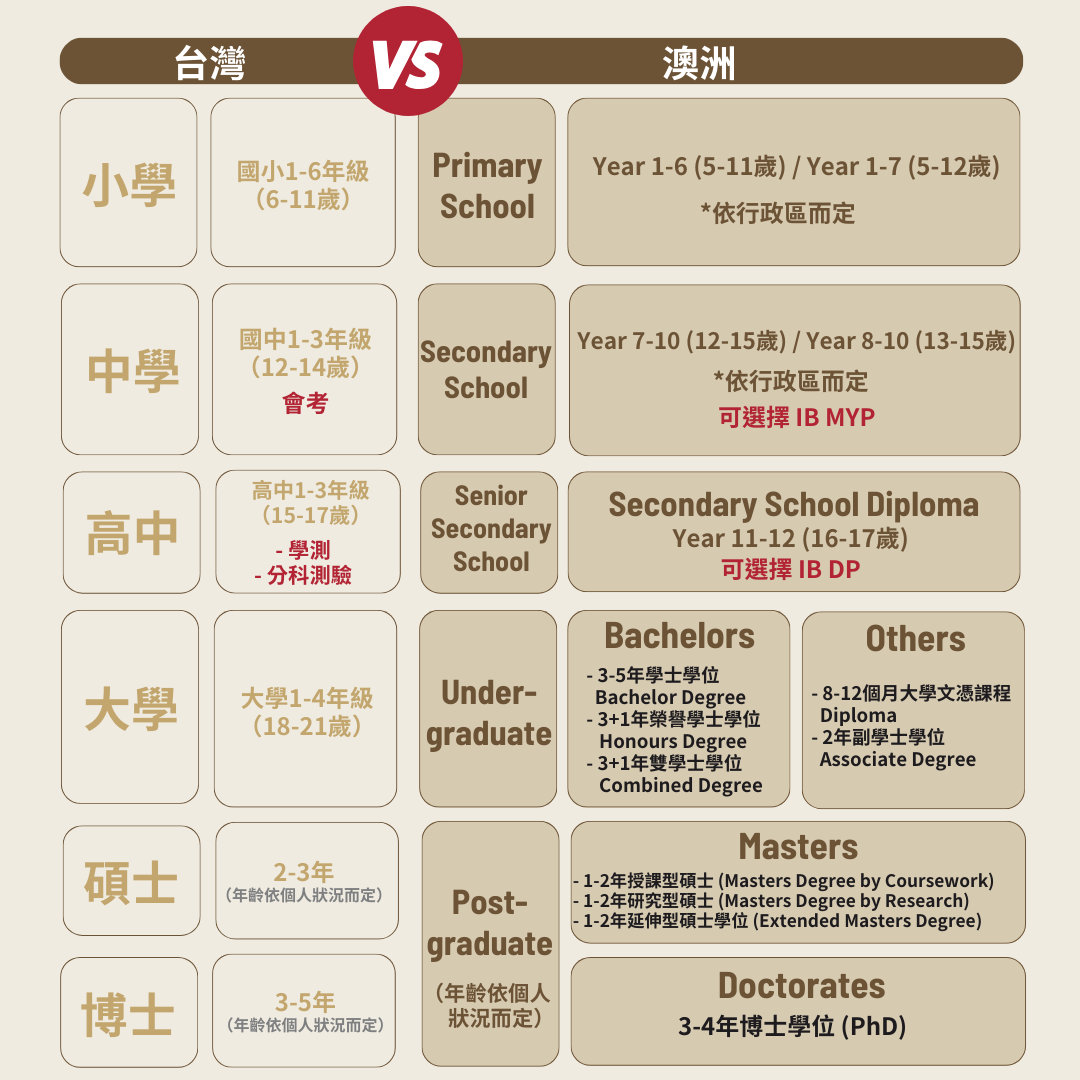
Taiwan’s education system vs. Australian education system
As one of the most popular study abroad destinations, Australia has a complete education system and many renowned research institutions and universities. Friendly admission requirements, great weather, and an international living and employment environment are the main reasons why students choose to study in Australia. The following provides an introduction and analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of the Australian academic system:
| Taiwan | Australia | |
| Elementary School Grade 1-6 (age 7-12) |
Primary School Years 1-6 Secondary School Years 7-10 |
小學課程 1-7年級 中學課程 8-10年級 |
| Jinior High Shcool Grade 7-9 (age 13-15) |
The following regions adopt this education system: Australian Capital Territory (ANT) Tasmania (TAS) Victoria (VIC) New South Wales (NSW) |
以下地區採用此學制: South Australia (SA) Northern Territory (NT) Queensland (QLD) Western Australia (WA) |
| Senior High School Grade 10-12 (age 16-18) |
高中課程 11-12年級 課程內容與評分將列入高等教育評分制度 |
|
| University 1-4 (age 19-22) |
大學文憑課程 University Diploma: 時長約為8-12個月。 副學士學位 Associate Degree: 時長約為1-2年,專業科目的基礎研究為主,採多元化的實務及理論並重取向。 學士學位 Bachelor Degree: 一般澳洲大學3~6年(例:文、法、商、理科需3年,工科4年,法律4~5年,而醫學則需6年)。 澳洲大學的課程內容皆為專業科目訓練,並無教授國內所謂的共同科目。 |
|
| Master 1-2 (age: depends) |
碩士證書/文憑 Graduate Certificate/Diploma: 專業學習課程,時長約半年至一年,可銜接碩士學位課程,但並非所有科系都有此課程。 碩士學位 Master Degree: 分為研究式/授課式,時長約為1-2年。 |
|
| Phd 3-5 years (age: depends) |
博士學位(Doctoral Degree): 以研究式為主。 |
|
Advantages: The social environment and public security in Canada are outstanding and the country’s citizens are generally friendly and gentle. The numerous opportunities for employment and education provided by CO-OP minimize the financial burden of education. Studying overseas in Canada has a lower cost than studying in the US or the UK. Because of its proximity to the United States, it has the advantage of connecting education and employment opportunities in the US. When combined with the welcoming immigration laws, it’s an ideal location to study for people who enjoy North American culture.
Disadvantages: Since most universities are public, applying for scholarships can be challenging. In comparison to the US and the UK, there are fewer university options. You must get used to the bitter cold and snowy conditions of the area.